Having trouble with kidney stones? Get help now
Kidney stones happen if minerals turn solid inside your kidneys – can bring sharp pain outta nowhere. Staying hydrated fights these issues while cutting risk later on.
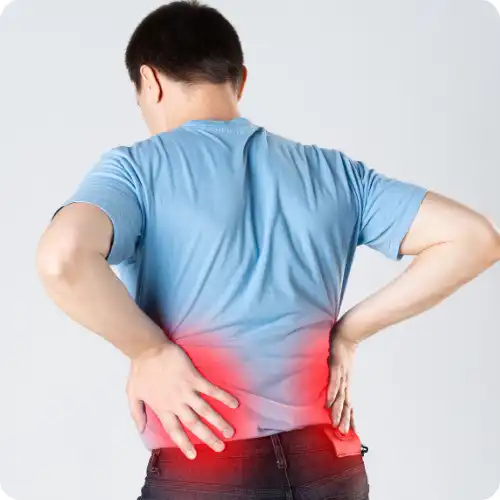
All About Kidney Stones
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones form when minerals pile up in your kidneys – often bringing sudden pain. These hard bits appear if you’re low on fluids, eat specific stuff, or have family history behind it. Pain might hit your back or stomach, urine could turn pinkish, plus a constant urge to pee shows up. Handling them may involve more liquids, meds, or treatments like sound wave breaks. Stay safe later by sipping water daily, eating different foods, while managing health conditions that stick around.
Painful Clues of Kidney Stones
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys, often causing severe pain. They develop due to factors like dehydration, diet, and genetic predisposition. Symptoms include intense back or abdominal pain, blood in urine, and frequent urination. Treatment options range from increased hydration and medications to medical procedures like lithotripsy. Preventing kidney stones involves staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet, and managing underlying health conditions.

Not All Stones Are the Same!
Types of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones happen when waste bits clump up inside your kidneys – usually bringing sharp, unexpected pain. Size increases if you don’t drink enough, eat certain foods, or carry genetic risks. Ache can show up in your side or belly, pee might go reddish, also urge to pee nonstop hits hard. Fixes mean chugging fluids, checking with a doc, or going for treatments such as shock wave blasts. Keeping them away takes steady water intake, sensible food choices, while handling health issues already there.
Calcium Stones
Formed due to high levels of calcium and oxalate in the urine, often linked to diet, dehydration, and medical conditions like hyperparathyroidism.
Uric Acid Stones
Develop when urine becomes too acidic due to a high-purine diet (red meat, shellfish), dehydration, or conditions like gout and diabetes.
Struvite Stones
Result from urinary tract infections (UTIs) caused by bacteria that increase ammonia levels in urine. and its painful also.
Cystine Stones
Formed due to a genetic disorder called cystinuria, where excess cystine leaks into the urine and crystallizes.
What Causes Kidney Stones?
Causes and Risk Factors of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard, mineral-based deposits that form in your kidneys. They develop when substances like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid crystallize due to imbalances in your urine composition. Understanding the causes and risk factors can help you take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing kidney stones. There are two types of the cuases we can consider

Dehydration
Not drinking enough water is one of the leading causes of kidney stones. When your urine is too concentrated, minerals can crystallize and stick together. Staying hydrated helps flush out these minerals before they form stones.

Medical Conditions
Conditions like urinary tract infections, gout, and inflammatory bowel diseases can all contribute to stone formation. Managing these conditions well is key to prevention.

Low Calcium Diet
It sounds surprising, but not getting enough calcium from food can increase your risk of stones. Dietary calcium binds oxalates in your gut, stopping them from reaching your kidneys.

Excessive Animal Protein
Eating too much red meat, poultry, or eggs can raise uric acid levels and lower urine pH. This creates an ideal environment for stone formation. Balance is key—try mixing in more plant-based options.

Obesity and Inactive Lifestyle
Being overweight or inactive can alter your body’s acid balance, encouraging stone growth. Regular movement and weight management can help protect your kidneys.

Genetics and Family History
If kidney stones run in your family, you may be more likely to get them too. While you can’t change your genes, you can take steps to minimize the risk through diet and prevention.

Inadequate Water Intake
Not drinking enough water is a leading cause of kidney stones. Dehydration leads to concentrated urine, allowing minerals to crystallize more easily. This is especially risky for people in hot climates or those with low fluid intake.

High-Protein,
Low-Fiber Diet
A diet high in animal protein raises uric acid levels, increasing the chance of stone formation. Low fiber intake affects digestion and body balance. Including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps reduce the risk.

High Sodium (Salt) Consumption
Excess salt in your diet causes your kidneys to excrete more calcium, which contributes to calcium-based stones. Since sodium is hidden in many processed foods, reducing overall intake is essential.
Recurrent Stone History
Having had a kidney stone before greatly raises your risk of another. Many experience recurrence within a few years without proper lifestyle changes, making regular monitoring and prevention key.

Prolonged Immobility or Bed Rest
Extended periods of immobility can lead to calcium buildup in the urine due to bone loss. Patients on bed rest should stay hydrated and follow movement routines to help prevent stones.

High Sugar and Fructose Intake
Diets high in sugar, especially fructose, increase calcium, oxalate, and uric acid in the urine—all major contributors to kidney stones. High sugar also contributes to obesity, further raising the risk.
What Causes Kidney Stones?
Causes and Risk Factors of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones form when minerals harden up in your kidneys. They stick together – like calcium, oxalate, or uric acid – usually if your urine’s off-kilter. Spotting what sets them off cuts the odds you’ll get one. Let’s split the reasons into two types
Main Causes

Dehydration
Not sipping enough water? That’s a top reason folks get kidney stones. If pee gets too strong, stuff like calcium might clump into crystals. Drinking plenty keeps things moving – so gunk doesn’t pile up. Hydration works by sweeping out junk early.

Medical Conditions
Conditions like urinary tract infections, gout, and inflammatory bowel diseases can all contribute to stone formation. Managing these conditions well is key to prevention.

Low Calcium Diet
It sounds surprising, but not getting enough calcium from food can increase your risk of stones. Dietary calcium binds oxalates in your gut, stopping them from reaching your kidneys.

Excessive Animal Protein
Eating plenty of red meat, poultry, or eggs can raise uric acid levels – this also makes urine more acidic. Since both changes happen together, they create a risk for kidney stones. To stay balanced, try adding plant-based options once in a while instead.

Obesity and Inactive Lifestyle
Carrying extra pounds or sitting too much might shift your body’s acidity, which could lead to stones. Staying active plus keeping a healthy weight supports kidney health.

Genetics and Family History
If kidney stones run in your family, you may be more likely to get them too. While you can’t change your genes, you can take steps to minimize the risk through diet and prevention.
Risk Factors

Inadequate Water Intake
Not drinking enough water is a leading cause of kidney stones. Dehydration leads to concentrated urine, allowing minerals to crystallize more easily. This is especially risky for people in hot climates or those with low fluid intake.

High-Protein,
Low-Fiber Diet
A diet high in animal protein raises uric acid levels, increasing the chance of stone formation. Low fiber intake affects digestion and body balance. Including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps reduce the risk.

High Sodium (Salt) Consumption
Excess salt in your diet causes your kidneys to excrete more calcium, which contributes to calcium-based stones. Since sodium is hidden in many processed foods, reducing overall intake is essential.

Recurrent Stone History
Having had a kidney stone before greatly raises your risk of another. Many experience recurrence within a few years without proper lifestyle changes, making regular monitoring and prevention key.

Prolonged Immobility or Bed Rest
Extended periods of immobility can lead to calcium buildup in the urine due to bone loss. Patients on bed rest should stay hydrated and follow movement routines to help prevent stones.

High Sugar and Fructose Intake
Diets high in sugar, especially fructose, increase calcium, oxalate, and uric acid in the urine—all major contributors to kidney stones. High sugar also contributes to obesity, further raising the risk.
How Are Kidney Stones Diagnosed?
Diagnosis and Tests for Kidney Stones
If you’re hurting bad, see blood when peeing, need to go often, feel sick, puke, or run a fever with shivers – might be kidney stones. Skip delays; get checked fast so things don’t worsen and you actually find out what’s wrong.
Urine and Blood Tests
Urine checks or blood work can spot mineral issues tied to kidney stones, giving key clues so doctors pick the right path for care.
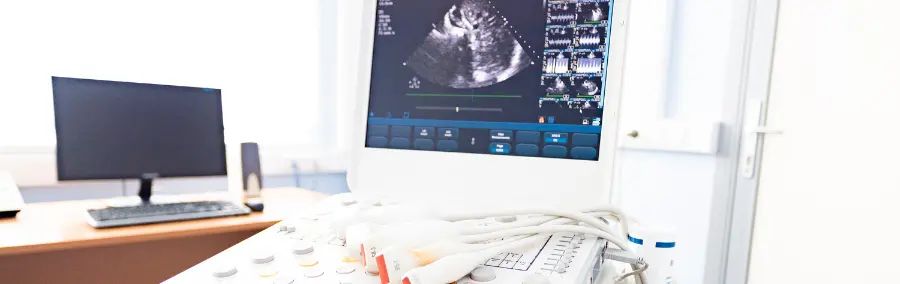
Ultrasound
Ultrasound finds kidney stones fast, using sound rather than X-rays. Doctors get clear views on stone size or where they sit – no radiation needed at all.
CT Scan
A CT scan gives sharp, cross-section views – making it a top choice for finding small kidney stones.
X-Ray
A single X-ray can spot big kidney stones while showing how they shift from one scan to the next – giving a fast way to see inside without hassle.
All About path.org
Kidney Stone Remover
Kidney stones develop when minerals plus salts clump together inside your kidneys – usually because you’re not drinking enough fluids or your body’s chemistry is off. These chunks might trigger sharp pain, you feel sick to your stomach, or mess with peeing as they travel down the urinary path. To deal with them, doctors could suggest increasing fluid intake, popping prescribed pills, or going through treatments like sound wave bursts it sound bad. Keeping yourself from getting them again means sipping plenty of liquids throughout the day, chowing down on varied whole foods, and cutting back on salty snacks or items that help stones grow.

Testimonials
What Our Customers Say
I struggled with kidney stones for weeks - then tried this patari remedy, so the pain eased fast. It worked way better than expected.

Blogs
Expert Articles on Kidney Stones

Check out top natural eats that help dodge kidney stones while giving your kidneys a lift. Lemon water? Yep -...

Check out top natural eats that help dodge kidney stones while giving your kidneys a lift. Lemon water? Yep -...

Kidney stones can be painful, but spotting early symptoms like back pain, painful urination, or blood in urine can help...

Discover effective Ayurvedic treatment for kidney stones at home using natural herbs, dietary changes, and holistic practices. Learn how to...






